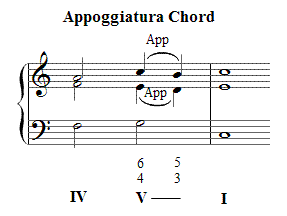
Passing 6 4 Chord Progression
Jonathan dean 17 573 views.
Passing 6 4 chord progression. Since the passing note in this example turns out to be the second degree of the scale the 6 4 chord we need to use will be a v. Applied chords secondary dominants. They make sense musically. These passing chords sound great between the 6 chord and 4.
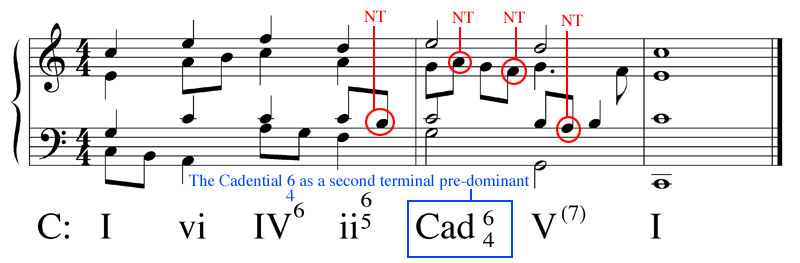
The passing 6 4 is another progression where you are allowed to use a second inversion 6 4 chord. 1 the neighboring 6 4 a k a. This basically occurs when the bass stays the same but the upper voices of the chord move to a 6 4 chord and back down to the original chord. A diatonic passing chord may be inserted into a pre existing progression that moves by a major or minor third in order to create more movement.
In music a passing chord is a chord that connects or passes between the notes of two diatonic chords. Pedal 6 4 2 the passing 6 4 3 the cadential 6 4. To begin let s take a look at how the number system works when it comes to chording. Second inversion triads 6 4 chords duration.
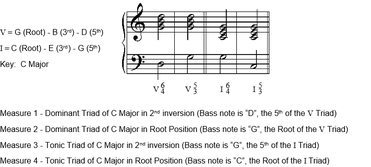
One of the upper voices will follow a similar passing tone movement in the opposite direction from the bass line one will remain stationary and one will move like a neighbor tone. Any chord that moves between one diatonic chord and another one nearby may be loosely termed a passing chord. The 1 5 6 4 chord progression is a simple chord progression that will unlock 100 s of familiar songs i am going to teach you how to play this progression and how to understand the chord number system so that you can play it in any key. Let s actually study real life applications of the 6 4 chord.
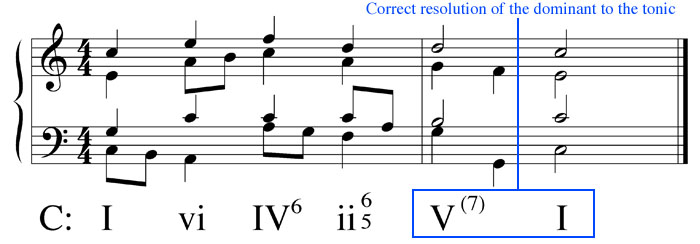
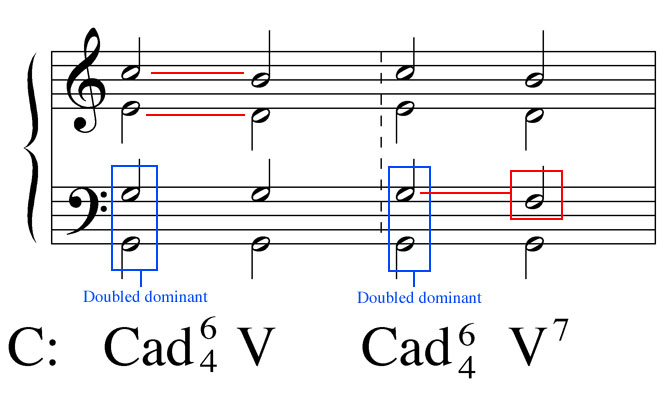
The passing 6 4 is another progression where you are allowed to use a second inversion 6 4 chord. The cadential 6 4 chord progression or when is a dominant triad in 2nd inversion is not a dominant triad in 2nd inversion a cadential 6 4 pronounced six four chord progression is a series of triads chords that are played to serve a purpose in the music. Unlike the cadential 6 4 where the bass note stays the same in a passing 6 4 the bass moves by step. These chords sound nice together.
Modulating in minor 3rds using a 1 5 6 4 chord progression duration. In this progression the other voices move predictably also. Unlike the cadential 6 4 where the bass note stays the same in a passing 6 4 the bass moves by step.